Chapter 5 The Behavior of Interest Rates
1) If
the expected return on ABC stock rises from 5 to 10 percent and the expected
return on CBS stock is unchanged, then the expected return of holding CBS stock
_____ relative to ABC stock and the demand for CBS stock _____.
A)
rises; rises B) rises; falls
C) falls; rises D) falls; falls
Answer:
D
5) If
the expected return on CBS stock rises from 5 to 10 percent and the expected
return on NBC stock rises from 12 to 18 percent, then the expected return of
holding CBS stock _____ relative to NBC stock and the demand for CBS stock
_____.
A)
rises; rises B) rises; falls
C) falls; rises D) falls; falls
Answer:
D
10) If
wealth increases, the demand for stocks _____ and that of long-term bonds
_____.
A)
increases; increases B) increases; decreases
C)
decreases; decreases D) decreases; increases
Answer:
A
15) If
interest rates on Treasury bonds are suddenly expected to shoot up, then, other
things equal, the demand for houses will _____ and that of Treasury bonds will
_____.
A)
increase; increase B) increase; decrease
C)
decrease; decrease D) decrease; increase
Answer:
B
20) The demand
for silver bullion decreases, other things equal, when
A)
the gold market is suddenly expected to boom.
B)
the market for silver bullion becomes more liquid.
C)
wealth grows rapidly.
D)
any of the above occurs.
Answer:
A
25) You
would be less willing to purchase U.S. Treasury bonds, other things equal, if
A)
brokerage fees for trading stocks decline.
B)
you expect interest rates to rise.
C)
gold becomes more liquid.
D)
any of the above occurs.
E)
either (b) or (c) of the above occurs.
Answer:
D
30) Holding
everything else constant,
A)
if an asset's risk rises relative to that of alternative assets, the demand
will fall.
B)
the more liquid an asset, relative to alternative assets, the greater will be
the demand.
C)
the higher the expected return relative to alternative assets, the greater will
be the demand.
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
D
35) If the
price of real estate becomes less volatile, then, other things equal, the demand
for stocks will _____ and that of antiques will _____.
A)
increase; increase B) increase; decrease
C)
decrease; decrease D) decrease; increase
Answer:
C
40) You
would be less willing to purchase U.S. Treasury bonds, other things equal, if
A)
you expect interest rates to rise.
B)
gold becomes more liquid.
C)
you inherit $1 million from your Uncle Harry.
D)
any of the above occurs.
E)
either (a) or (b) of the above occurs.
Answer:
E
45) When the price of a bond is below the equilibrium
price, there is an excess _____ for (of) bonds and price will _____.
A)
demand; rise B) demand; fall
C) supply; fall D) supply; rise
Answer:
A
50) When the interest rate on a bond is below the
equilibrium interest rate, in the bond market there is excess _____ and the
interest rate will _____.
A)
demand; rise B) demand; fall
C) supply; fall D) supply; rise
Answer:
D
55) When
the interest rate rises, either the demand for bonds ______ or the supply of
bonds
_____.
A)
increases; increases B) increases; decreases
C)
decreases; decreases D) decreases; increases
Answer:
D
60) When stock prices become less volatile, the
______ curve for bonds shifts to the _____.
A)
demand; right B) demand; left
C) supply; left D) supply; right
Answer:
B
65) If people expect real estate prices to decrease
significantly, the _____ curve for bonds will shift to the _____.
A)
demand; right B) demand; left
C) supply; left D) supply; right
Answer:
A
70) When bond interest rates become more volatile,
the demand for bonds _____ and the interest rate _____.
A)
increases; rises B) increases;
falls C) decreases; falls D) decreases; rises
Answer:
D
75) When people begin to expect a run up in large
stock market, the demand curve for bonds shifts to the _____ and the interest
rate _____.
A)
right; rises B) right; falls
C) left; falls D) left; rises
Answer:
D
80) When prices in the stock market become more uncertain,
the demand curve for bonds shifts to the _____ and the interest rate _____.
A)
right; rises B) right; falls
C) left; falls D) left; rises
Answer:
B
85) When real income increases, the demand curve
for money shifts to the _____ and the interest rate _____.
A)
right; rises B) right; fall
C) left; falls D) left; rises
Answer:
A
90) When the price level _____, the demand curve
for money shifts to the _____ and the interest rate _____.
A)
falls; left; falls
B)
falls; right; falls
C)
falls; left; rises
D)
rises; right; rises
E)
rises; right; falls
Answer:
D
95) When the Fed increases the money stock, the
money supply curve shifts to the _____ and the interest rate _____.
A)
right; rises B) right; falls
C) left; falls D) left; rises
Answer:
B
100) When stock prices become _____ volatile,
the demand curve for bonds shifts to the _____ and the interest rate _____.
A)
more; right; rises
B)
more; left; falls
C)
less; left; falls
D)
less; left; rises
E)
more; right; falls
Answer:
E
105) When
the growth rate of the money supply is decreased, interest rates will fall
immediately
if
the liquidity effect is _____ than the other money supply effects and there is
_____
adjustment
of expected inflation.
A) larger;
fast B) larger; slow C) smaller; slow D) smaller; fast
Answer: D
110) If
the Fed wants to permanently lower interest rates, then it should raise the
rate of money growth if
A)
there is fast adjustment of expected inflation.
B) there is slow adjustment of
expected inflation.
C) the liquidity effect is smaller
than the expected inflation effect.
D) the liquidity effect is larger
than the other effects.
Answer: D
115) The
theory of asset demand provides a framework for deciding what factors cause the
demand curve for bonds shift.
These factors include changes in the
A)
wealth of investors.
B)
liquidity of bonds relative to alternative assets.
C)
expected returns on bonds relative to alternative assets.
D)
risk of bonds relative to alternative assets.
E)
all of the above.
Answer:
E
120) Holding
the expected return on bonds constant, an increase in the expected return on
common stocks would _____ the demand for bonds, shifting the demand curve to
the _____.
A)
decrease; left B) decrease; right
C) increase; left D) increase; right
Answer:
A
125) A
decrease in the expected rate of inflation will _____ the expected return on
bonds relative to the that on _____ assets, and shift the _____ curve to the
left.
A)
reduce; financial; demand
B)
reduce; real; demand
C)
raise; financial; supply
D)
raise; real; supply
E)
raise; real; demand
Answer:
E
130) All
else the same, an increase in the volatility of the stock market causes the demand
for bonds to _____ and the demand curve to shift to the _____.
A)
fall; right B) fall, left C) rise; right D) rise; left
Answer:
C
135) Factors that cause the demand curve
for bonds to shift to the right include
A)
a decrease in the inflation rate.
B) an increase in the volatility of
stock prices.
C) an increase in the liquidity of
stocks.
D) all of the above.
E) only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer: E
140) Factors
that cause the demand curve for bonds to shift to the left include
A) an increase in the volatility of
stock prices.
B) a decrease in the expected
returns on stocks.
C) a decrease in the inflation
rate.
D) a decrease in the riskiness of
stocks.
Answer: D
145) Factors that can cause the supply curve
for bonds to shift to the right include
A)
an expansion in overall economic activity.
B)
an increase in expected inflation.
C)
an increase in government deficits.
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
D
150) Factors that can cause the supply
curve for bonds to shift to the left include
A)
an expansion in overall economic activity.
B)
an increase in expected inflation.
C)
a decrease in government deficits.
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
C
155) The loanable funds framework is
easier to use when analyzing the effects of changes in _____, while the
liquidity preference framework provides a simpler analysis of the effects from
changes in income, the price level, and the supply of _____.
A)
expected inflation; bonds B) expected inflation; money
C)
government budget deficits, bonds D) government budget deficits, money
Answer:
B
160) A lower level of income causes the demand
for money to _____ and the demand curve for money to shift to the _____.
A)
decrease; right B) decrease; left
C) increase; right D) increase; left
Answer:
B
165) A higher level of income causes the
demand for money to _____ and the interest rate to _____.
A)
decrease; decrease B) decrease; increase
C)
increase; decrease D) increase; increase
Answer:
D
170) Holding everything else equal, an
increase in the money supply causes
A)
interest rates to decline initially.
B)
interest rates to increase initially.
C)
bond prices to increase initially.
D)
both (a) and (c) of the above.
E)
both (b) and (c) of the above.
Answer:
D
175) Of the four effects on interest
rates from an increase in the money supply, the one that works in the opposite
direction of the other three is the
A)
liquidity effect. B) income effect.
C)
price level effect. D) expected inflation effect.
Answer:
A
180) The supply curve for bonds has the usual
upward slope, indicating that as the price _____, ceteris paribus, the _____
increases.
A)
falls, supply B) falls, quantity supplied
C)
rises, supply D) rises, quantity supplied
Answer:
D
185) In a contracting economy with
declining wealth, the demand for bonds _____ and the demand curve for bonds
shifts to the _____.
A)
rises, right B) rises, left
C) falls, right D) falls, left
Answer:
D
190) An increase in the liquidity of
bonds results in a _____ in demand for bonds and the demand curve shifts to the
_____.
A)
rise, right B) rise, left C) fall, right D) fall, left
Answer:
A
195) Higher government deficits _____
the supply of bonds and shift the supply curve to the _____.
A)
increase, left B) increase, right
C) decrease, left D) decrease, right
Answer:
B
200) When the inflation rate is expected
to increase, the _____ for bonds falls, while the _____ curve shifts to the
right.
A)
demand, demand B) demand, supply
C)
supply, demand D) supply, supply
Answer:
B
205) During a business cycle
contraction, the supply of bonds shifts to the _____ as businesses perceive
fewer profitable investment opportunities, while the demand for bonds shifts to
the _____ as a result of the decrease in wealth.
A)
right, left B) right, right
C) left, left D) left, right
Answer:
C
210) In the Keynesian liquidity
preference framework, a lower level of income causes the demand for money to
_____ and the demand curve to shift to the _____.
A)
increase, left B) increase, right
C) decrease, left D) decrease, right
Answer:
C
215) If the liquidity effect is smaller
than the other effects, and the adjustment to expected inflation is slow, then
the
A)
interest rate will fall.
B)
interest rate will rise.
C)
interest rate will initially fall but eventually climb above the initial level
in response to an increase in money growth.
D)
interest rate will initially rise but eventually fall below the initial level
in response to an increase in money growth.
Answer:
C
Figure 5-1
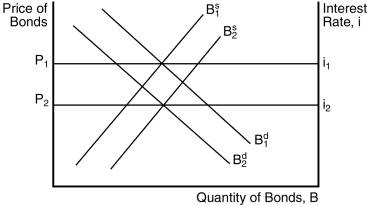
220) In Figure 5-1, an increase in the
expected inflation rate causes the
A)
interest rate to increase from i1 to i2.
B)
interest rate to decrease from i2 to i1.
C)
demand curve for bonds to shift to the left.
D)
both (a) and (c) of the above.
E)
both (b) and (c) of the above.
Answer:
D
225) In Figure 5-1, one factor that
would not have caused the demand for bonds to decrease (shift to the left) is
A)
a decrease in the expected return on bonds relative to other assets.
B)
an increase in wealth.
C)
a decrease in wealth.
D)
an increase in the riskiness of bonds relative to other assets.
Answer:
B
230) In Figure 5-1, factors that could
cause the supply of bonds to shift to the right include:
A)
a decrease in government budget deficits.
B)
an increase in expected inflation.
C)
a recession.
D)
expectations of fewer profitable investment opportunities.
Answer:
B
235) In Figure 5-1, factors that could
cause the demand for bonds to decrease (shift to the left) include:
A)
an increase in the riskiness of bonds relative to other assets.
B)
a decrease in the expected rate of inflation.
C)
expectations of higher interest rates in the future.
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
D
240) In Figure 5-1, the increase in the
interest rate from i1 to i2 due to an increase in the
expected inflation rate is called the
A)
Fisher effect. B) liquidity
effect. C) income effect. D) Keynes effect.
Answer:
A
Figure 5-2
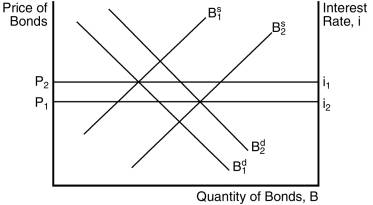
245) In Figure 5-2, one factor that would
not have caused the supply of bonds to increase is
A)
an increase in government budget deficits.
B)
a decrease in expected inflation.
C)
expectations of more profitable investment opportunities.
D)
a business cycle expansion.
Answer:
B
250) In Figure 5-2, factors that could
cause the demand for bonds to increase include:
A)
an increase in the riskiness of bonds relative to other assets.
B)
a decrease in the expected return on bonds relative to other assets.
C)
an increase in wealth.
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
C
Figure 5-3

255) In Figure 5-3, one factor not
responsible for the decline in the interest rate is
A)
a decline the price level.
B)
a decline in income.
C)
an increase in income.
D)
a decline in the expected inflation rate.
Answer:
C
260) In Figure 5-3, the decline in the
interest rate from i1 to i2 can be explained by
A)
a decrease in income.
B)
a decrease in the expected price level.
C)
an increase in money growth.
D)
both (a) and (b) of the above.
E)
both (a) and (c) of the above.
Answer:
D
Figure 5-5

265) Figure 5-5 illustrates the effect
of an increased rate of money supply growth. From the figure, one can conclude that the
A)
the Fisher effect is dominated by the liquidity effect and interest rates
adjust slowly to changes in expected inflation.
B)
the liquidity effect is dominated by the Fisher effect and interest rates
adjust slowly to changes in expected inflation.
C)
the liquidity effect is dominated by the Fisher effect and interest rates adjust quickly to
changes in expected inflation.
D)
the Fisher effect is smaller than the expected inflation effect and interest
rates adjust quickly to changes in expected inflation.
Answer:
C