Chapter
6 The Risk and Term Structure of Interest Rates
1) The term structure of interest
rates is
A)
the relationship among interest rates of different bonds with the same
maturity.
B)
the structure of how interest rates move over time.
C)
the relationship among the term to maturity of different bonds.
D)
the relationship among interest rates on bonds with different maturities.
Answer:
D
5) Which of the following long-term
bonds currently has the lowest interest rate?
A)
Corporate Aaa bonds B) U.S. Treasury bonds
C)
Corporate Aa bonds D) Corporate Baa bonds
Answer:
B
10) When the Treasury bond market becomes more
liquid, other things equal, the demand curve for corporate bonds shifts to the
_____ and the demand curve for Treasury bonds shifts to the _____.
A)
right; right B) right; left
C) left; right D) left; left
Answer:
C
15) The interest rate on municipal bonds falls
relative to the interest rate on Treasury securities when
A)
there is a major default in the municipal bond market.
B)
income tax rates are raised.
C)
municipal bonds become less widely traded.
D)
corporate bonds become riskier.
E)
none of the above occur.
Answer:
B
20) If income tax rates were lowered, then
A)
the prices of municipal bonds would fall.
B)
the prices of Treasury bonds would rise.
C)
the interest rate on Treasury bonds would rise.
D)
both (a) and (b) would occur.
Answer:
D
25) A plot of the interest rates on default-free
government bonds with different terms to maturity is called
A)
a risk-structure curve. B) a term-structure curve.
C)
a yield curve. D) an interest-rate curve.
Answer:
C
30) If the expected path of one-year interest rates
over the next four years is 5 percent, 4 percent, 2 percent, and 1 percent,
then the expectations theory predicts that today's interest rate on the
four-year bond is
A)
1 percent. B) 2 percent.
C)
4 percent. D) none of the above.
Answer:
D
35) If the yield curve slope is flat, the liquidity
premium theory (assuming a mild preference for shorter-term bonds) indicates
that the market is predicting
A)
a mild rise in short-term interest rates in the near future and a mild decline
further out in the future.
B)
constant short-term interest rates in the near future and further out in the
future.
C)
a mild decline in short-term interest rates in the near future and a continuing
mild decline further out in the future.
D)
constant short-term interest rates in the near future and a mild decline
further out in the future.
Answer:
C
40) If a corporation begins to suffer large losses,
then
A)
the default risk on the corporate bond will increase and the bond's return will
become more uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will
fall.
B)
the default risk on the corporate bond will increase and the bond's return will
become less uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will
fall.
C)
the default risk on the corporate bond will decrease and the bond's return will
become less uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will
fall.
D)
the default risk on the corporate bond will decrease and the bond's return will
become less uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will
rise.
Answer:
A
45) The theory of asset demand predicts that
because the expected return on corporate bonds falls as their relative
riskiness rises, the demand for corporate bonds will _____ and the demand for
default-free bonds will _____.
A)
rise; rise B) rise; fall C) fall; rise D) fall; fall
Answer:
C
50) Bonds with relatively high risk of default are
called
A)
Brady bonds. B) junk bonds.
C)
zero coupon bonds. D) investment grade bonds.
Answer:
B
55) A risk premium is sometimes called a
A)
default premium. B) rating premium.
C)
liquidity premium. D) junk premium.
Answer:
C
60) The relationship among interest rates on bonds
with identical default risk, but of different maturities is called the
A)
time-risk structure of interest rates. B) liquidity structure of interest rates.
C)
bond demand curve. D) yield curve.
Answer:
D
65) When yield curves are flat,
A)
long-term interest rates are above short-term interest rates.
B)
short-term interest rates are above long-term interest rates.
C)
short-term interest rates are about the same as long- term interest rates.
D)
medium-term interest rates are above both short-term and long-term interest
rates.
E)
medium-term interest rates are below both short-term and long-term interest
rates.
Answer:
C
70) According to the expectations theory of the
term structure
A)
when the yield curve is steeply upward sloping, short- term interest rates are
expected to rise in the future.
B)
when the yield curve is downward sloping, short-term interest rates are
expected to decline in the future.
C)
yield curves should be as equally likely to slope downward as slope upward.
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
D
75) According to the expectations theory of the
term structure
A)
when the yield curve is steeply upward sloping, short-term interest rates are
expected to rise in the future.
B)
when the yield curve is downward sloping, short-term interest rates are
expected to remain relatively stable in the future.
C)
investors have strong preferences for short-term relative to long-term bonds,
explaining why yield curves typically slope upward.
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
A
80) According to the segmented markets theory of
the term structure
A)
bonds of one maturity are close substitutes for bonds of other maturities,
therefore, interest rates on bonds of different maturities move together over
time.
B)
the interest rate for each maturity bond is determined by supply and demand for
that maturity bond.
C)
investors' strong preferences for short-term relative to long-term bonds
explains why yield curves typically slope downward.
D)
all of the above.
Answer:
B
85) According to the liquidity premium theory of
the term structure
A)
when short-term interest rates are expected to rise in the future, the yield
curve will be upward sloping.
B)
when short-term interest rates are expected to decline moderately in the
future, the yield curve is likely to be flat.
C)
when short-term interest rates are expected to decline significantly in the
future, the yield curve is likely to be downward sloping,
D)
all of the above.
E)
only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
D
90) According to the liquidity premium theory of
the term structure, a flat yield curve indicates that
A)
short-term interest rates are expected to rise in the future.
B)
short-term interest rates are expected to remain unchanged in the future.
C)
short-term interest rates are expected to decline moderately in the future.
D)
short-term interest rates are expected to decline sharply in the future.
Answer:
C
95) U.S. government bonds have no default risk
because
A)
they are backed by the full faith and credit of the federal government.
B)
the federal government can increase taxes or even just print money to pay its
obligations.
C)
they are backed with gold reserves.
D)
all of the above.
E)
of only (a) and (b) of the above.
Answer:
B
100) Which of the following statements
are true?
A)
An increase in default risk on corporate bonds lowers the demand for these
bonds, but increases the demand for default-free bonds.
B)
The expected return on corporate bonds decreases as default risk increases.
C)
A corporate bond's return becomes more uncertain as default risk increases.
D)
As their relative riskiness increases, the expected return on corporate bonds
decreases relative to the expected return on default-free bonds.
E)
All of the above are true statements.
Answer:
E
105) Which of the following statements
are true?
A)
An increase in default risk on corporate bonds lowers the demand for these
bonds, but increases the demand for default-free bonds.
B)
The expected return on corporate bonds decreases as default risk increases.
C)
A corporate bond's return becomes less uncertain as default risk increases.
D)
Only (a) and (b) of the above are true statements.
E)
Only (a) and (c) of the above are true statements.
Answer:
D
110) Following the stock market crash of
1987, the spread between interest rates on junk bonds and U.S. government bonds
A)
fell by two percentage points to four percentage points.
B)
fell by six percentage points to ten percentage points.
C)
rose by two percentage points to six percentage points.
D)
rose by six percentage points to ten percentage points.
Answer:
C
115) Which of the following statements
are true?
A)
An increase in tax rates will increase the demand for Treasury bonds, lowering
their interest rates.
B)
Because the tax-exempt status of municipal bonds was of little benefit to bond
holders when tax rates were low, they had higher interest rates than U.S.
government bonds before World War II.
C)
Interest rates on municipal bonds will be higher than comparable bonds without
the tax exemption.
D)
Only (a) and (b) are true statements.
Answer:
B
120) When the yield curve is upward
sloping,
A)
the expectations theory suggests that short-term interest rates are expected to
rise.
B)
the expectations theory suggests that short-term interest rates are expected to
fall.
C)
the segmented markets theory suggests that short-term interest rates are
expected to fall.
D)
the liquidity premium theory suggests that short-term interest rates are
expected to fall.
Answer:
A
125) It cannot explain the empirical
fact that interest rates on bonds of different maturities tend to move
together.
A)
segmented markets theory
B)
expectations theory
C)
liquidity premium theory
D)
both (a) and (b) of the above
E)
both (a) and (c) of the above
Answer:
A
130) According to the liquidity premium
theory
A)
a steeply rising yield curve indicates that short-term interest rates are
expected to remain unchanged in the future.
B)
a moderately rising yield curve indicates that short-term interest rates are
not expected to change much in the future.
C)
a flat yield curve indicates that short-term interest rates are expected to
rise moderately in the future.
D)
only (a) and (b) of the true.
Answer:
B
Figure 6-2
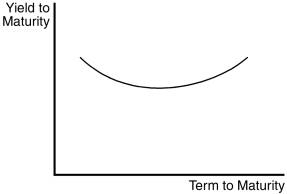
135) The U-shaped yield curve in Figure
6-2 indicates that _____ interest rates are expected to _____
A)
short-term; rise in the near-term and fall later on.
B)
short-term; fall sharply in the near-term and rise later on.
C)
short-term; fall moderately in the near-term and rise later on.
D)
short-term; remain unchanged in the near-term and rise later on.
Answer:
B